Dotarem® (gadoterate meglumine) injection is an ionic, macrocyclic gadolinium-based contrast agent (GBCA). The first marketing authorization of Dotarem® was approved in 2013 in the United States.2 Since then, Dotarem® has been used in clinical practice, delivering effective MR contrast-enhanced examination.3-6
Dotarem (gadoterate meglumine) Injection Important Safety Information
WARNING: RISK ASSOCIATED WITH INTRATHECAL USE and NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS (NSF)
Risk Associated with Intrathecal Use Intrathecal administration of gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. DOTAREM is not approved for intrathecal use.
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis GBCAs increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of DOTAREM in these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrasted MRI or other modalities. NSF may result in fatal or debilitating fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle and internal organs. The risk for NSF appears highest among patients with:
Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (e.g. age > 60 years, hypertension, diabetes), estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) through laboratory testing. For patients at highest risk for NSF, do not exceed the recommended DOTAREM dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug from the body prior to any re-administration. |
Dotarem® by Guerbet, a flagship brand with over 30 years of real-world experience.1,2
Due to its chemical structure, Dotarem® offers high thermodynamic and kinetic stability to minimize the risk of free gadolinium (Gd3 ) released. 7,8
Stability and Experience
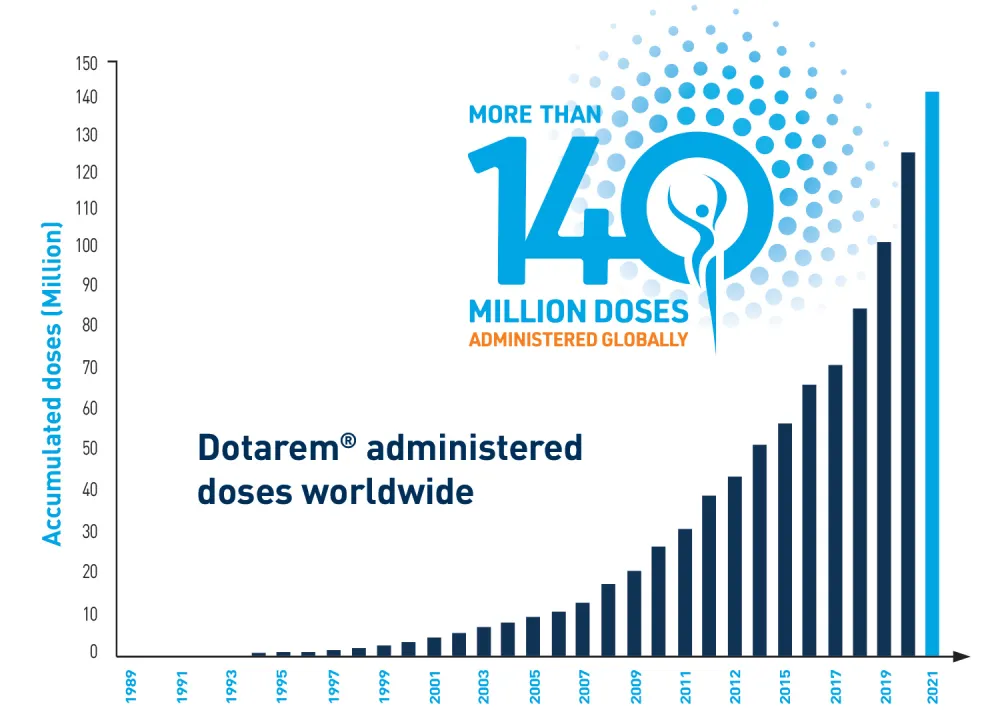
Dotarem® by Guerbet has been trusted for clinical use by radiologists for over 30 years** and is known for high molecular stability.7 With more than 140 million global doses administered,9 Dotarem delivers an effective contrast-enhanced MR examination with dependable consistency.2
- Patented manufacturing process 10
- More than 140 million doses administered globally with zero unconfounded case of NSF. 2,9
- Following repeated administrations, no visible T1 signal intensity detected on non-contrast images within the brain.11-15
Driven by its commitment to advance radiology, Guerbet Diagnostic Imaging has designed a comprehensive and complete portfolio of products and solutions for diagnostic imaging.
Learn more about Dotarem®
Complete the form below to download the material
References
- Val M. Runge et al., The developmental history of the gadolinium chelates as intravenous contrast media for magnetic resonance. Invest Radiol. 2011 Dec;46(12):807-16.
- Dotarem [package insert]. Princeton, NJ: Guerbet LLC; March 2025
- Braun J., et al. Baseline characteristics, diagnostic efficacy, and periexaminational safety of IV gadoteric acid MRI in 148,489 patients. Acta Radiol. 2020.Jul;61(7):910-920.
- Soyer P., et al. Observational study on the safety profile of gadoterate meglumine in 35,499 patients: The SECURE study. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2017.Apr;45(4):988–997.
- Chang DH., et al. Safety of gadoterate meglumine in over 1600 children included in the prospective observational SECURE study. Acta Radio. 2019. Nov;60(11):1450–1456.
- Maravilla K., et al. Comparison of Gadoterate Meglumine and Gadobutrol in the Diagnosis of Primary Brain Tumors: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Intraindividual Crossover Study (the REMIND Study). AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017.Sept;38(9):1681-1688
- Port M., et al. Efficiency, thermodynamic and kinetic stability of marketed gadolinium chelates and their possible clinical consequences: a critical review. Biometals. 2008.21(4):469–490
- Frenzel T., et al. Stability of Gadolinium-Based Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agents in Human Serum at 37°C. Invest Radiol. 2008.Dec;43(12):817-288.
- Data on file, Guerbet internal data, 2025.
- Patent US 9,655,983
- Radbruch A et al. Gadolinium retention in the dentate nucleus and globus pallidus is dependent on the class of contrast agent. Radiology. 2015 Jun;275(3):783-91.
- Radbruch A et al. Intraindividual analysis of signal intensity changes in the dentate nucleus after consecutive serial applications of linear and macrocyclic gadolinium-based contrast agents. Invest Radiol. 2016 Nov;51(11):683-690.
- Eisele P et al. Lack of increased signal intensity in the dentate nucleus after repeated administration of a macrocyclic contrast agent in multiple sclerosis: An observational study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Sep;95(39): e4624.
- Radbruch A et al. Pediatric brain: no increased signal intensity in the dentate nucleus on unenhanced T1-weighted MR images after consecutive exposure to a macrocyclic gadolinium-based contrast agent. Radiology. 2017 Jun;283(3):828-836.
- Tibussek D et al. Gadolinium brain deposition after macrocyclic gadolinium administration: a pediatric case-control study. Radiology. 2017 Oct;285(1):223-30. Epub 2017 Jun 21. GU09250018
Dotarem® (gadoterate meglumine) Injection
WARNING: RISK ASSOCIATED WITH INTRATHECAL USE and NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS (NSF)
Risk Associated with Intrathecal Use Intrathecal administration of gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. DOTAREM is not approved for intrathecal use.
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis GBCAs increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of DOTAREM in these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrasted MRI or other modalities. NSF may result in fatal or debilitating fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle and internal organs. The risk for NSF appears highest among patients with:
Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (e.g. age > 60 years, hypertension, diabetes), estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) through laboratory testing. For patients at highest risk for NSF, do not exceed the recommended DOTAREM dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug from the body prior to any re-administration. |
Indications and Usage
DOTAREM® (gadoterate meglumine) injection is a prescription gadolinium-based contrast agent indicated for intravenous use with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in brain (intracranial), spine and associated tissues in adult and pediatric patients (including term neonates) to detect and visualize areas with disruption of the blood brain barrier (BBB) and/or abnormal vascularity.
Contraindications
History of clinically important hypersensitivity reactions to DOTAREM.
Warnings and Precautions
- Risk Associated with Intrathecal Use: Intrathecal administration of GBCAs can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. The safety and effectiveness of DOTAREM have not been established with intrathecal DOTAREM is not approved for intrathecal use.
- Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis: GBCAs increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the Avoid use of DOTAREM among these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrast MRI or other modalities.
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions have been reported with DOTAREM, involving cardiovascular, respiratory, and/or cutaneous Some patients experienced circulatory collapse and died.
- Before DOTAREM administration, assess all patients for any history of a reaction to contrast media, bronchial asthma and/or allergic disorders. These patients may have an increased risk for a hypersensitivity reaction to DOTAREM.
- Gadolinium Retention: Gadolinium is retained for months or years in several organs. The highest concentrations have been identified in the bone, followed by other organs (e.g. brain, skin, kidney, liver and spleen). While clinical consequences of gadolinium retention have not been established in patients with normal renal function, certain patients might be at higher risk. These include patients requiring multiple lifetime doses, pregnant and pediatric patients, and patients with inflammatory conditions Minimize repetitive GBCA imaging studies, particularly closely spaced studies when possible.
- Acute Kidney Injury: In patients with chronically reduced renal function, acute kidney injury requiring dialysis has occurred with the use of The risk of acute kidney injury may increase with increasing dose of the contrast agent; administer the lowest dose necessary for adequate imaging.
- Extravasation and Injection Site Reactions: Ensure catheter and venous patency before the injection of DOTAREM. Extravasation into tissues during DOTAREM administration may result in tissue irritation.
Adverse Reactions
- In clinical trials, the most frequent adverse reactions that occurred in > 2% of patients who received Dotarem included: nausea, headache, injection site pain, injection site coldness and rash.
- Serious adverse reactions in the Postmarketing experience have been reported with use of DOTAREM or other GBCAs. Serious adverse reactions include but are not limited to arrhythmia, cardiac arrest, respiratory arrest, pharyngeal edema, laryngospasm, bronchospasm, coma, convulsion, acute pancreatitis, acute respiratory distress syndrome, pulmonary edema.
Use in Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: GBCAs cross the human placenta and result in fetal exposure and gadolinium Use only if imaging is essential during pregnancy and cannot be delayed.
- Lactation: There are no data on the presence of gadoterate in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk However, published lactation data on other GBCAs indicate that
0.01 to 0.04% of the maternal gadolinium dose is present in breast milk. - Pediatric Use: The safety of DOTAREM has not been established in preterm No dosage adjustment according to age is necessary in pediatric patients.
- Geriatric Use: use of DOTAREM in elderly patients should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of impaired renal function and concomitant disease or other drug therapy. No age-related dosage adjustment is necessary.
- Renal Impairment: No DOTAREM dosage adjustment is recommended for patients with renal
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
Please see the full Prescribing Information, including the Medication Guide, for additional important safety information.
