Dotarem Remains an Industry Standard for Contrast Imaging for Over 30 Years*
Dotarem (Gadoterate Meglumine) Injection Important Safety Information
WARNING: RISK ASSOCIATED WITH INTRATHECAL USE and NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS (NSF)
Risk Associated with Intrathecal Use Intrathecal administration of gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. DOTAREM is not approved for intrathecal use.
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis GBCAs increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of DOTAREM in these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrasted MRI or other modalities. NSF may result in fatal or debilitating fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle and internal organs. The risk for NSF appears highest among patients with:
Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (e.g. age > 60 years, hypertension, diabetes), estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) through laboratory testing. For patients at highest risk for NSF, do not exceed the recommended DOTAREM dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug from the body prior to any re-administration. |

Low Incidence of Immediate Adverse Events in Clinical Uses1-7
Dotarem® has been tested in more than studies - it has also withstood the test of real-world clinical uses.1
- 4.0% in clinical trials (N=2822)
- 0.7% considered serious
- 1% in postmarketing studies (N>150,000)
- 0.007% reported spontaneously worldwide
(>50 million doses)- 0.0023% incidence rate of serious adverse events
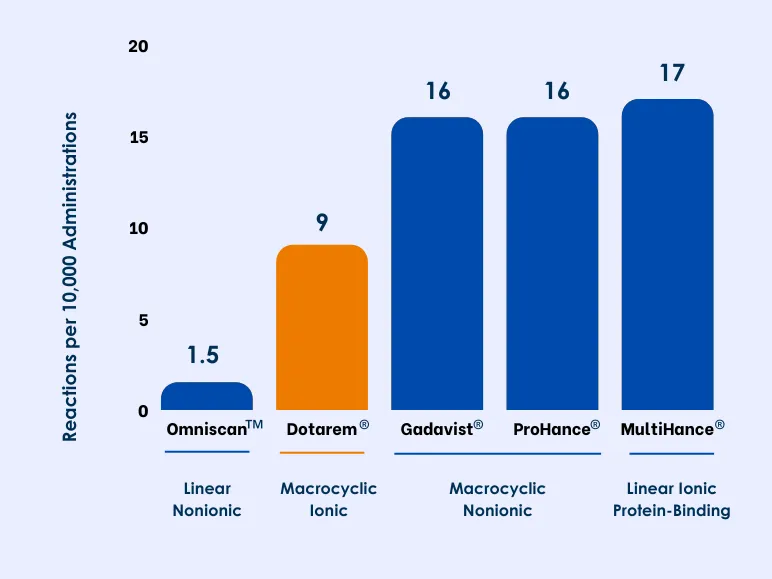
How Does Dotarem® Compare to Other GBCAs Sold in the US?
Differences in reaction rates among GBCAs have been difficult to demonstrate because of the large number of patients needed to show statistically significant differences for such rare events. In a systematic review and meta-analysis of 9 studies, including 716,978 GBCA administrations, rates of immediate allergic-like AEs per 10,000 administrations among macrocyclic agents were lowest for ionic Dotarem® vs nonionic Gadavist® and ProHance®.8
A Stable Clinical Profile Established for Children11
The safety and efficacy of Dotarem have been established in pediatric patients from birth (term neonates ≥37 weeks gestational age) to 17 years of age.12 In a pediatric study of 1,568 patients, image quality was rated either good or very good by radiologists in 98.4% of cases when using Dotarem.9
Pediatric Radiologists are Switching to Dotarem10
58% (15 of 26) of pediatric radiology departments surveyed switched their GBCA for reasons that included:
- Brain gadolinium deposition concerns (73%)
- Improved safety profile (47%)
- Improved stability (33%)
- NSF concerns (20%)
- Cost (7%)
Of the 58% that recently switched, 53% (8 of 15) switched to DOTAREM
Another 23% (6 of 26) were considering switching and of those, 83% (5 of 6) reported that they planned to switch to DOTAREM
*Dotarem was launched globally in 1989 and approved by the FDA for use in the US in 2013.
References
- de Kerviler E et al. Adverse reactions to gadoterate meglumine: review of over 25 years of clinical use and more than 50 million doses. Invest Radiol. 2016 Sep;51(9):544-51.
- Briand et al. Efficacy and safety of the macrocyclic complex Gd-DOTA in Children: Results of a Multi-Centre Study. Proceedings of the 29th Congress of the European Society of Pediatric Radiology. 1992; 128.
- Briand Y. Daily Paediatric Use of MRI Contrast Agents: Results of a Multi-Centre Survey. Proceedings of the 29th Congress of the European Society of Pediatric Radiology. 1992.
- Ishiguchi T & Takahashi S. Safety of gadoterate meglumine (Gd-DOTA) as a contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging: results of a post-marketing surveillance study in Japan. Drugs R D. 2010;10(3):133-45.
- Emond S & Brunelle F. Gd-DOTA administration at MRI in children younger than 18 months of age: immediate adverse reactions. Pediatr Radiol. 2011 Nov;41(11):1401-6.
- Maurer M et al. Tolerability and diagnostic value of gadoteric acid in the general population and in patients with risk factors: results in more than 84,000 patients. Eur J Radiol. 2012 May;81(5):885-90.
- Soyer et al. Observational Study on the Safety Pro le of Gadoterate Megluminein 35,499 Patients: The SECURE Study. J. Magn. Reson. Imag. 2017; 45, 988-997
- Behzadi AH, Zhao Y, Farooq Z, Prince MR. Immediate allergic reactions to gadolinium-based contrast agents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiology. 2018;286(2):471-482.
- De-Hua, Chang, and Pracros Jean-Pierre. "Safety of Gadoterate Meglumine in over 1600 Children Included in the Prospective Observational SECURE Study." Acta Radiologica, 2019.
- Mithal LB, Patel PS, Mithal D, Palac HL, Rozenfeld MN. Use of gadolinium-based magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents and awareness of brain gadolinium deposition among pediatric providers in North America. Pediatr Radiol. 2017;47(6):657-664.
- Dotarem [package insert]. Princeton, NJ: Guerbet LLC; March 2025
GU09250019
WARNING: RISK ASSOCIATED WITH INTRATHECAL USE and NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS (NSF)
Risk Associated with Intrathecal Use Intrathecal administration of gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. DOTAREM is not approved for intrathecal use.
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis GBCAs increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of DOTAREM in these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrasted MRI or other modalities. NSF may result in fatal or debilitating fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle and internal organs. The risk for NSF appears highest among patients with:
Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (e.g. age > 60 years, hypertension, diabetes), estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) through laboratory testing. For patients at highest risk for NSF, do not exceed the recommended DOTAREM dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug from the body prior to any re-administration. |
Indications and Usage
DOTAREM® (gadoterate meglumine) injection is a prescription gadolinium-based contrast agent indicated for intravenous use with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in brain (intracranial), spine and associated tissues in adult and pediatric patients (including term neonates) to detect and visualize areas with disruption of the blood brain barrier (BBB) and/or abnormal vascularity.
Contraindications
History of clinically important hypersensitivity reactions to DOTAREM.
Warnings and Precautions
- Risk Associated with Intrathecal Use: Intrathecal administration of GBCAs can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. The safety and effectiveness of DOTAREM have not been established with intrathecal DOTAREM is not approved for intrathecal use.
- Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis: GBCAs increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the Avoid use of DOTAREM among these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrast MRI or other modalities.
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions have been reported with DOTAREM, involving cardiovascular, respiratory, and/or cutaneous Some patients experienced circulatory collapse and died.
- Before DOTAREM administration, assess all patients for any history of a reaction to contrast media, bronchial asthma and/or allergic disorders. These patients may have an increased risk for a hypersensitivity reaction to DOTAREM.
- Gadolinium Retention: Gadolinium is retained for months or years in several organs. The highest concentrations have been identified in the bone, followed by other organs (e.g. brain, skin, kidney, liver and spleen). While clinical consequences of gadolinium retention have not been established in patients with normal renal function, certain patients might be at higher risk. These include patients requiring multiple lifetime doses, pregnant and pediatric patients, and patients with inflammatory conditions Minimize repetitive GBCA imaging studies, particularly closely spaced studies when possible.
- Acute Kidney Injury: In patients with chronically reduced renal function, acute kidney injury requiring dialysis has occurred with the use of The risk of acute kidney injury may increase with increasing dose of the contrast agent; administer the lowest dose necessary for adequate imaging.
- Extravasation and Injection Site Reactions: Ensure catheter and venous patency before the injection of DOTAREM. Extravasation into tissues during DOTAREM administration may result in tissue irritation.
Adverse Reactions
- In clinical trials, the most frequent adverse reactions that occurred in > 2% of patients who received Dotarem included: nausea, headache, injection site pain, injection site coldness and rash.
- Serious adverse reactions in the Postmarketing experience have been reported with use of DOTAREM or other GBCAs. Serious adverse reactions include but are not limited to arrhythmia, cardiac arrest, respiratory arrest, pharyngeal edema, laryngospasm, bronchospasm, coma, convulsion, acute pancreatitis, acute respiratory distress syndrome, pulmonary edema.
Use in Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: GBCAs cross the human placenta and result in fetal exposure and gadolinium Use only if imaging is essential during pregnancy and cannot be delayed.
- Lactation: There are no data on the presence of gadoterate in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk However, published lactation data on other GBCAs indicate that
0.01 to 0.04% of the maternal gadolinium dose is present in breast milk.
- Pediatric Use: The safety of DOTAREM has not been established in preterm No dosage adjustment according to age is necessary in pediatric patients.
- Geriatric Use: use of DOTAREM in elderly patients should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of impaired renal function and concomitant disease or other drug therapy. No age-related dosage adjustment is necessary.
- Renal Impairment: No DOTAREM dosage adjustment is recommended for patients with renal
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
Please see the full Prescribing Information, including the Medication Guide, for additional important safety information.
